Introduction: Decarbonizing India's Steel Industry
Global Context and India's Role
The global steel industry plays a significant role in carbon emissions, contributing to climate change. The International Energy Agency's Breakthrough Agenda Report 2023 indicates that the steel sector is not on track to meet net-zero emissions by mid-century, with total emissions still rising. This is particularly concerning given that less than 1 million tons of near-zero emission steel is currently being produced globally, and the industry accounts for 7-9% of global carbon emissions. The steel sector needs a substantial reduction in emissions to align with climate targets, requiring a decrease of around 25% by 2030. (1)
In India, the steel industry's emissions are a major component of the country's industrial carbon footprint. As one of the largest steel producers in the world, India faces the challenge of balancing its industrial growth with its commitments to climate change mitigation. The World Economic Forum's Net-Zero Industry Tracker 2023 underlines India's efforts in reducing emission intensity and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources in line with its climate commitments.
The Significance of Decarbonization in India
Decarbonizing the steel industry in India is not only an environmental imperative but also a strategic necessity. The introduction of global policies such as the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) impacts Indian steel exports, influencing the country's approach to decarbonization. Adapting to these changes requires innovation and a steadfast commitment to sustainable practices.
India's journey towards decarbonizing its steel industry involves embracing technological innovations, policy frameworks, and global cooperation. As reported by McKinsey, adopting an approach that combines scrap, direct reduced iron (DRI), and electric arc furnaces (EAF) using hydrogen is considered the most viable option for achieving carbon-neutral steel production. The transition to green hydrogen-based steel production is emerging as a key solution, despite the high costs of green hydrogen production. This shift is driven by decreasing costs for electrolyzers and renewable electricity, and the rising penalties for carbon dioxide emissions under systems like the EU ETS. (2)
The complete transformation of India's steel industry towards sustainability will be a complex yet crucial endeavor, requiring the integration of cutting-edge technologies, supportive policies, and collaborative efforts both domestically and globally.
India’s Climate Goals and the Steel Industry
Overview of India's Climate Commitments India, as a signatory to the Paris Agreement, has made significant commitments to mitigate climate change. In its updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs), India aims to reduce the emissions intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030, relative to 2005 levels. (3) (4) This ambitious target reflects India's dedication to aligning with global efforts to limit warming to 1.5°C. However, India's reliance on coal-generated electricity remains a challenge due to economic and developmental reasons, with a 4% rise in CO2 emissions from burning low-quality coal reported in the first half of 2023 compared to the same period in 2022. (5)
The Steel Industry's Role in India's Carbon Footprint
The steel industry is a significant contributor to India's carbon emissions. Decarbonizing this sector is crucial for India to meet its climate goals. The steel industry's traditional reliance on coal and energy-intensive processes makes it a focal point for India's decarbonization efforts. Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage(CCUS) technologies, in which GAS LAB specializes, are becoming increasingly relevant in this context. CCUS can significantly reduce emissions from steel production, complementing other decarbonization strategies like the shift to hydrogen-based steel production and the use of electric arc furnaces. This aligns with global trends, where the adoption of scrap, direct reduced iron (DRI), and electric arc furnaces (EAF) using hydrogen is considered the most viable option for carbon-neutral steel production. (2)
Policy Frameworks Driving Decarbonization
NITI Aayog’s Initiatives: NITI Aayog, as the premier policy think tank of the Government of India, plays a crucial role in crafting strategies for the country's development, including its approach to decarbonization. Its reports on carbon capture and industrial decarbonization offer key recommendations and targets that are instrumental in shaping India's climate policies. (6)
● Key Recommendations and Targets: The reports emphasize the importance of transitioning to low-carbon technologies across various industries, with a specific focus on carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) as a vital tool for industrial decarbonization. NITI Aayog advocates for increased investment in CCUS technologies and research, development of regulatory frameworks, and creation of market mechanisms to incentivize carbon capture implementation.
● Role in Shaping Policy and Strategy: NITI Aayog's recommendations serve as a guide for government policies and initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The think tank's input is crucial in forming comprehensive strategies that balance economic growth with environmental sustainability, influencing national policies on energy, industry, and climate change.
CBAM and Its Influence: The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) is a policy tool designed to level the playing field for European Union (EU) producers by imposing a carbon cost on imports from countries with less stringent environmental regulations. It aims to prevent carbon leakage, where industries shift to countries with looser environmental rules. (7)
● Explanation of CBAM: CBAM functions by charging importers for the carbon emissions associated with the goods they bring into the EU. This mechanism is intended to encourage producers in non-EU countries to reduce their carbon emissions if they want to maintain competitive access to the EU market.
● Impact on Indian Steel Exports: CBAM significantly impacts Indian steel exports to the EU, compelling the Indian steel industry to adopt cleaner production methods to avoid additional costs. This has a direct influence on India’s decarbonization strategies, pushing the industry towards more sustainable practices and technologies like carbon capture and storage. The mechanism underscores the need for Indian industries to innovate and align with global environmental standards to remain competitive in key international markets. The policies and recommendations from NITI Aayog, combined with the external pressures from mechanisms like CBAM, are shaping the trajectory of India's efforts in decarbonizing its steel industry. These frameworks not only guide national strategies but also underscore the importance of global cooperation and alignment in addressing climate change challenges.
Technological Innovations and Advances in the Indian Steel Industry
Current State of Technology for Reducing Carbon Emissions
The Indian steel industry is gradually integrating advanced technologies to reduce its carbon footprint. The traditional methods, predominantly based on coal and other fossil fuels, are being reassessed in light of global and national environmental commitments. Emerging technologies, such as energy-efficient furnaces, waste heat recovery systems, and improved process controls, are increasingly being adopted. However, the industry still faces challenges in fully transitioning to low-carbon technologies due to financial and infrastructural constraints.
Carbon Capture Solutions in Steel Decarbonization
The integration of CCUS technologies in the steel industry is an area where GAS LAB's sustainable expertise can play a pivotal role. By capturing and storing CO2 emissions from steel production processes, it can significantly reduce the industry's carbon footprint. The successful implementation of CCUS in steel manufacturing would mark a significant step towards achieving India's climate targets while maintaining industrial growth.
For India to meet its ambitious climate goals, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. This includes strengthening climate targets, adopting emission reduction plans across the economy, and securing international support for advanced technologies and infrastructure development. The steel industry, being one of the most carbon-intensive sectors, will play a crucial role in this transition, with technologies like CCUS leading the way towards a more sustainable future.
CO2 Utilization in the Steel Industry
CO2 utilization, a component of the broader Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) strategy, presents a promising opportunity for the steel industry to not only reduce emissions but also to generate revenue. This approach involves converting captured CO2 into valuable products or services. In the context of the steel industry, CO2 can be utilized in several innovative ways:
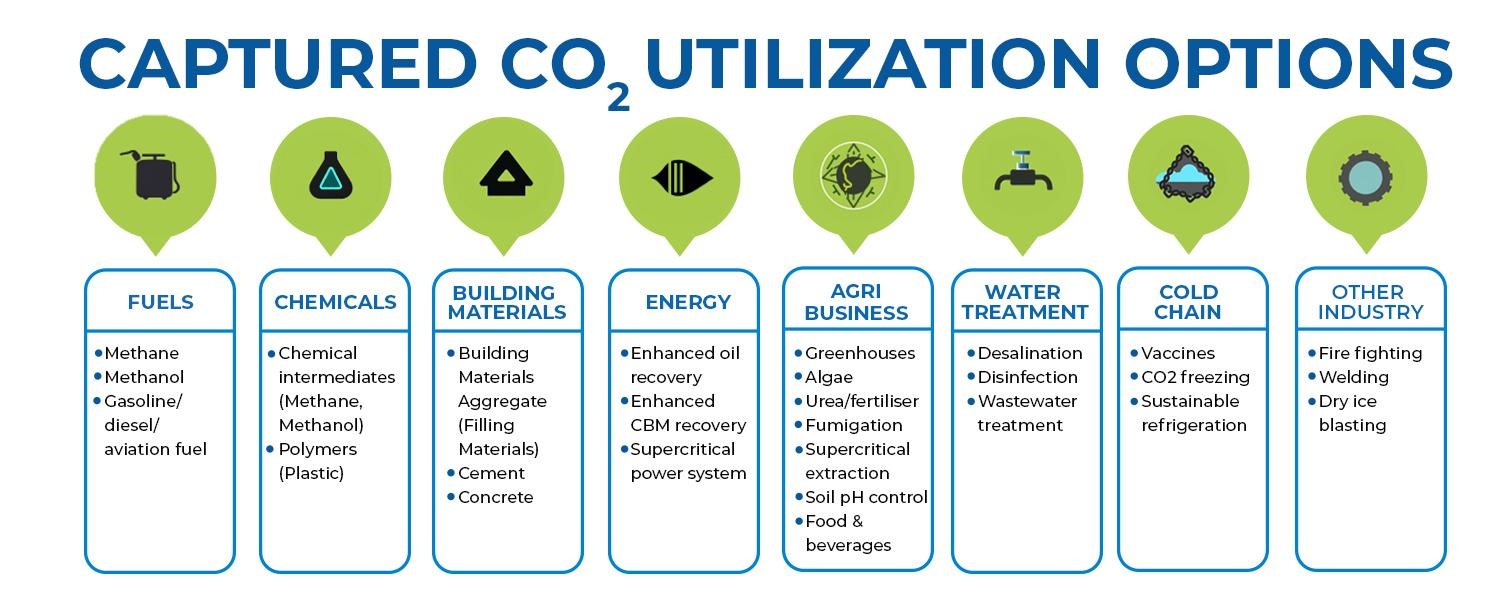
CO2 utilization not only helps in mitigating environmental impact but also aligns with the concept of a circular economy, turning waste into resource. For the steel industry, it offers a pathway to both sustainability and profitability.
Case Studies and Current Projects in the Indian Steel Industry
Innovative Practices and Collaborations
The Indian steel industry, in its pursuit of sustainability and decarbonization, has embarked on various innovative projects and collaborations. These endeavors highlight the industry's commitment to environmental responsibility and technological advancement. Tata Steel, a leading player in the Indian steel sector, has made significant strides in carbon capture and utilization. Their project at the Jamshedpur plant is a notable example, where CO2 emissions from the blast furnace gas are captured and utilized for bioethanol production. This project exemplifies the practical application of carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies in the steel industry. (8)
JSW Steel has focused on integrating sustainable practices into its operations. The company has invested in energy-efficient technologies and is exploring renewable energy sources for its plants. This shift towards greener energy sources is a critical step in reducing the overall carbon footprint of the steel manufacturing process. (9)
Opportunities in Decarbonizing India's Steel Industry
Driving Innovation and Technological Advancement
● The push towards decarbonization presents significant opportunities for technological innovation within the steel industry. Advancements in areas like carbon capture and storage (CCS) and hydrogen-based steel production not only offer pathways to reduce emissions but also open new avenues for research and development. This innovation is crucial for India to meet its ambitious target of reducing emissions intensity by 45% by 2030 compared to 2005 levels. (4)
Economic Growth and Job Creation
● Transitioning to sustainable practices can spur economic growth and create new job opportunities. The steel industry's move towards green technologies can lead to the emergence of new sectors and skillsets, offering a potential boost to employment. The development of a green economy aligns with India's broader sustainable development goals, contributing to overall economic prosperity.
Global Leadership in Sustainable Steel Production
● India has the potential to become a global leader in sustainable steel production. By adopting innovative practices and setting ambitious targets, India can showcase a model for sustainable industrial growth. This leadership role can enhance India's influence in international climate negotiations and partnerships.
International Collaboration and Access to Funding
The opportunities presented by the decarbonization of the steel industry are multidimensional, offering India a chance to innovate, grow economically, and assert global leadership in sustainable industrial practices. These opportunities align with the nation's broader goals of sustainable development and climate action.
Conclusion: India's Steel Industry and the Future of Decarbonization
India's steel industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the need for environmental sustainability and aligned with the country's climate goals. The progress in adopting technologies like carbon capture and exploring hydrogen-based production reflects India's commitment to reducing industrial emissions, in line with its target to decrease emissions intensity by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels.
Looking forward, the industry's journey is set to be shaped by continued innovation, policy support, and global cooperation. While challenges remain, the opportunities for economic growth, global leadership in sustainable practices, and technological advancements are vast. India's proactive approach in embracing these changes positions it as a key player in the global move towards sustainable steel production.
Reference Links
(1) https://www.iea.org/reports/breakthrough-agenda-report-2023
(3) https://www.energypolicy.columbia.edu/cop28-assessing-indias-progress-against-climate-goals/
(4) https://pib.gov.in/PressReleaseIframePage.aspx?PRID=1847812
(5) https://www.dw.com/en/what-are-indias-climate-goals-at-cop28/a-67650531
(6) https://www.niti.gov.in/sites/default/files/2022-11/CCUS-Report.pdf
(9) https://www.jsw.in/groups/JSW-energy-sustainability-framework-measuring-success-climate-change